Pearls of Knowledge: Junctional Rhythms

Dysrhythmias: Junctional rhythms
Pearls of Knowledge © BrainyNurses.com
In junctional rhythm, the SA node is no longer in control and the AV node becomes the pacemaker by default due to the property of automaticity. Because the AV node is a less reliable pacemaker, the development of junctional rhythm is cause for concern. The analysis of junctional rhythms is determined by the P waves and the rate.

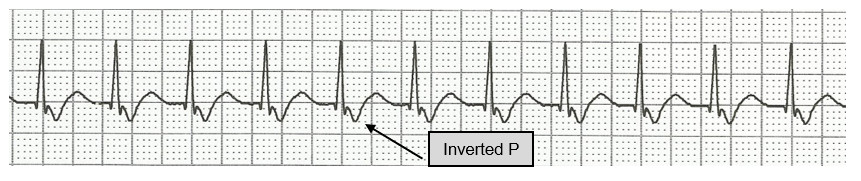
Because the impulse starts in the AV node, the atria are depolarized in a retrograde manner resulting in an inverted P wave in the upright (positive) leads (such as lead II).

Analysis of inverted P waves (in the upright leads)
- Inverted P wave before the QRS when the atria depolarize before the ventricles.
- Inverted P wave buried in the QRS when the atria and ventricles depolarize at the same time.
- Inverted P wave after the QRS when the ventricles depolarize before the atria.
Analysis of rate
- Junctional rhythm: HR 40-60 BPM.
- Accelerated junctional rhythm: HR 60-100 BPM.
- Junctional tachycardia: HR greater than 100 BPM.
Rhythm strips
Junctional rhythm. HR=52 BPM. QRS=0.08.

Accelerated junctional rhythm. HR=58 BPM. QRS=0.08.

Junctional tachycardia. HR=115 BPM. QRS=0.08.